- Meal Delivery
Shop by Category
TOP PROVIDERS
POPULAR SEARCHES
Meal Finder Tool

Use our meal finder quiz to find the best meal delivery service for you.
- Vitamin & Supplements
- Deals
- About
- Blog
Vegan Meals Delivered
Vegan Meals Delivered
Are you looking to try to integrate more vegan meals into your weekly meals? Our team of experts have compared and rated vegan meal delivery services, and have identified the best options according to price and nutritional profile. Have a look at some of Australia’s best vegan meal delivery options, with key information provided so you can compare choices and find the right match for your needs!
Featured Product

Compare Vegan Meals Delivered
Advertiser Discolure Advertiser DiscolureGet up to $200 off first 6 boxes! Get Deal
At least 5 recipes each week tagged Vegetarian, some of which are Vegan meals free of any animal products.
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD, NT, SA, WA
$10.50/serve
$200 OFF Your First 8 Orders Get Deal
Soulara is a 100% vegan, plant-based meal delivery service with all meals, drinks and snacks free of any animal products.
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD, NT, SA, TAS
$10.90/serve
Get $220 OFF first 5 boxes! Get Deal
At least 3 Vegan recipes each week. These recipes exclude all animal products - no meat, eggs, dairy or other animal products.
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD, SA, TAS
$10.99/serve
$20 OFF when you spend $100 Get Deal
100% fully vegan meals that are certified organic, whole-food, gluten-free and oil-free. Shop a rotating menu using fresh and local ingredients.
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD, SA, TAS
$12.95/serve
Get $140 OFF the first 5 boxes! Get Deal
Dinnerly is one of the most affordable meal-kit providers in Australia. Their menu includes at least 6 Vegan recipes each week.
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD, NT, SA, TAS
$7.49/serve
High-quality, flavourful and delicious meals that are convenient and affordable. High Protein, No Added Gluten, Vegetarian, Vegan, and Dairy Free.
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD, SA, WA, TAS
$11.00/serve
15% off your order! Get Deal
All dishes are 100% vegan and crafted with fresh and authentic ingredients and use plant-based proteins.
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD, SA
$11.95/serve
Get $50 OFF your order! Get Deal
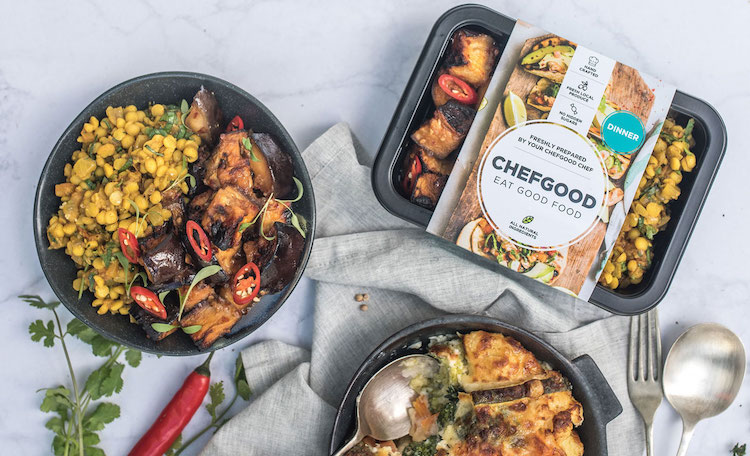
Choose between 5 and 20 meals each week on the Chefgood Vegan meal plan.
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD, SA
$11.20/serve
Save up to $120 on your first 6 orders! Get Deal
The Vegan Booster Pack is a fixed set of 14 protein-rich, plant-based meals that are 100% vegan and ready to eat.
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD, SA, WA
$10.35/serve
25% OFF your first order! Get Deal
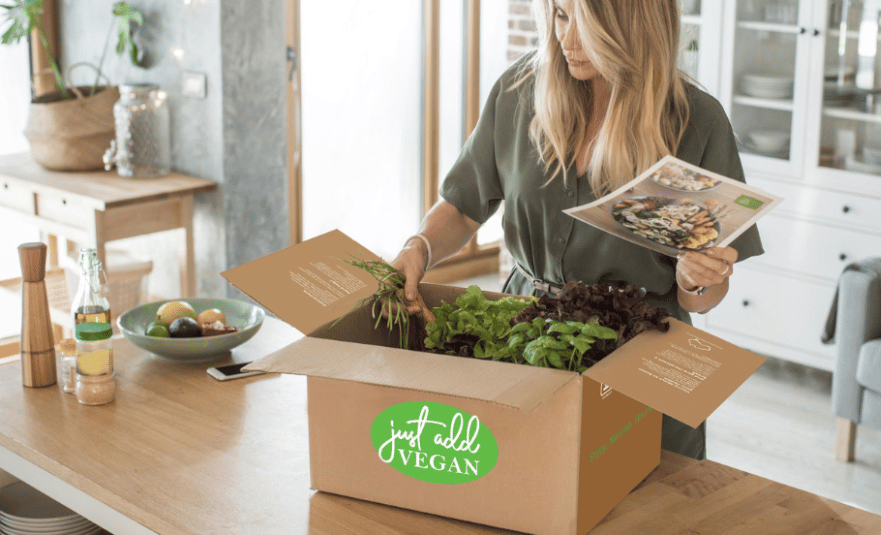
Just Add Vegan has now reopened and updated their meal offering as of May 2024! Just Add Vegan is a …
NSW, ACT
$14.00/serve
100% vegan, chef-designed meals with a repertoire of over 100 recipes to choose from.
NSW, VIC
$13.00/serve
Vegan, plant-based meal range offering ready-made meals with dietitian-designed menus.
NSW
$11.00/serve
Dineamic is a carbon neutral company that prioritizes sourcing foods locally, and offers pre-made meals that you can pick and …
NSW, VIC, QLD, SA, WA, TAS
$11.50/serve
Iku is 100% vegan and specialises in pre-made macrobiotic plant-based meals full of nutrients and flavour. You can pick and …
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD
$11.95/serve
$30 off your first order Get Deal
Gourmet Dinner Service prioritizes making healthy meals with 100% real ingredients ridiculously convenient. Founded by masterchef Janel Horton, Gourmet Dinner …
NSW, VIC, ACT, QLD
$11.00/serve
Providoor supplies restaurant quality, snap frozen meals that preserve the flavour and freshness of the food. Featuring meals prepared by …
NSW, VIC, QLD
$9.00/serve